Executive Summary
This document describes the recent Kaseya VSA cyberattack. This massive attack was launched against around 50 ‘managed services’ providers by a threat actor that is associated with REvil ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) group. This attack happened due to an unpatched zero-day vulnerability in Kaseya’s VSA software.
Current Exploit Strategy
The REvil Ransoware known as Sodinokibi targeted MSP’s with thousands of customers and appears to be a Kaseya VSA supply-chain attack. Kaseya VSA is a cloud-based MSP platform that allows providers to perform patch management and monitoring for the customers. The exploit targets unpatched Kaseya software with a potential authentication bypass by using Windows legitimate software.
No current freeware decryptor
There are currently no decryptors available for the latest infection to restore important files. However, a huge ransom is demanded for the provision of a special decryptor from REvil Ransomware.
REvil Ransomware as a Service (RaaS)
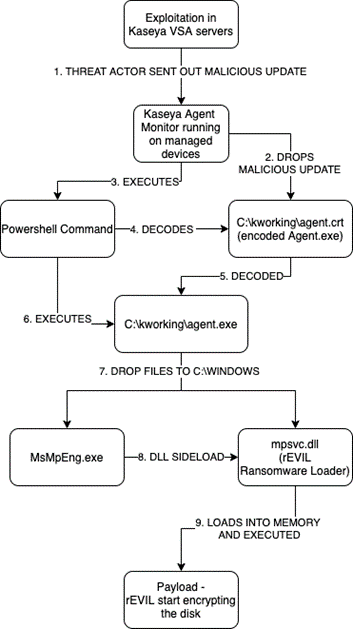
REvil Ransomwares spreads via a malicious update which was released to Kaseya VSA servers. Once the execution is performed by Powershell Command, it will install the encoded Agent.exe into the endpoint. Tasks scheduled will run the malicious exe file and create a DLL sideload into the memory for execution. After the execution of DLL, the endpoint will be compromised and start encrypting the disk by REvil Ransomware.
The Ransomware Payload
The payload configuration file is embedded in the ransomware encoded in RC4 (Encryption Algorithm which commonly uses wireless routers) with the key mXT1QFyEUbrxc4c bP84jbN5wrHeqmFXt.


Additional Threats
Types of configurations that avoids encrypting files from lists of directories, system files, extension files, terminate processes and terminate services;
Directories:
“program files”, “appdata”, “mozila”, “$windows.~ws”, “application data”, $windows.~bt”, “google”, “$recycle.bin”, “windows.old”, “programdata”, “system volume information”, “program files (x86)”, “boot”, “tor browser”, “windows”, “intel”, “perflogs”, “msocache”
System Files:
“ntldr”, “thumbs.db”, “bootsect.bak”, “autorun.inf”, “ntuser.dat.log”, “boot.ini”, “iconcache.db”, “bootfont.bin”, “ntuser.dat”, “ntuser.ini”, “desktop.ini”
Extension Files:
“ps1”, “ldf”, “lock”, “theme”, “msi”, “sys”, “wpx”, “cpl”, “adv”, “msc”, “scr”, “bat”, “key”, “ico”, “dll”, “hta”, “deskthemepack”, “nomedia”, “msu”, “rtp”, “msp”, “idx”, “ani”, “386”, “diagcfg”, “bin”, “mod”, “ics”, “com”, “hlp”, “spl”, “nls”, “cab”, “exe”, “diagpkg”, “icl”, “ocx”, “rom”, “prf”, “themepack”, “msstyles”, “lnk”, “icns”, “mpa”, “drv”, “cur”, “diagcab”, “cmd”, “shs”
Terminate Process:
“encsvc”, “powerpnt”, “ocssd”, “steam”, “isqlplussvc”, “outlook”, “sql”, “ocomm”, “agntsvc”, “mspub”, “onenote”, “winword”, “thebat”, “excel”, “mydesktopqos”, “ocautoupds”, “thunderbird”, “synctime”, “infopath”, “mydesktopservice”, “firefox”, “oracle”, “sqbcoreservice”, “dbeng50”, “tbirdconfig”, “msaccess”, “visio”, “dbsnmp”, “wordpad”, “xfssvccon”
Terminate Services:
“veeam”, “memtas”, “sql”, “backup”, “vss”,”sophos”, “svc$”, “mepocs”
Victims of REvil Ransomware
Kaseya
Indication of Compromise
IOCs for REvil / Kaseya:
File:
SHA256: d55f983c994caa160ec63a59f6b4250fe67fb3e8c43a388aec60a4a6978e9f1e
agent.exe
IOCs for Spam Campaign:
File:
SHA1: 7B6621202AC7795E89891B7BD65E769BA6C267C5
SecurityUpdates.exe
Network:
hxxp://45[.]153[.]241[.]113/download/pload[.]exe
hxxp://31[.]42[.]177[.]52/dpixel
hxxp://31[.]42[.]177[.]52/submit.php
Domain
18.223.199.234 | 123vrachi.ru |
161.35.239.148 | 12starhd.online |
101gowrie.com | datacenters-in-europe.com |
dpo-as-a-service.com | journeybacktolife.com |
dr-pipi.de | 35.226.94.113 |
dutchcoder.nl | 162.253.124.162 |
Hash Value Sha1
• 45AEBD60E3C4ED8D3285907F5BF6C71B3B60A9BCB7C34E246C20410CF678FC0C
• 2093C195B6C1FD6AB9E1110C13096C5FE130B75A84A27748007AE52D9E951643
• 0299E3C2536543885860C7B61E1EFC3F
• 040818B1B3C9B1BF8245F5BCB4EEBBBC
• 18786BFAC1BE0DDF23FF94C029CA4D63
• 4A91CB0705539E1D09108C60F991FFCF
• 561CFFBABA71A6E8CC1CDCEDA990EAD4
• 5A97A50E45E64DB41049FD88A75F2DD2
• 7D1807850275485397CE2BB218EFF159
• 7EA501911850A077CF0F9FE6A7518859
• 835F242DDE220CC76EE5544119562268
• 849FB558745E4089A8232312594B21D2
• 8535397007ECB56D666B666C3592C26D
• BE6C46239E9C753DE227BF1F3428E271
• 0912B7CECFBE82D6903A8A0DC421C285480E5CAA
• 13D57ABA8DF4C95185C1A6D2F945D65795EE825B
• 1BCF1AE39B898AAA8B6B0207D7E307B234614FF6
• 20E3A0955BACA4DC7F1F36D3B865E632474ADD77
• 3C2B0DCDB2A46FC1EC0A12A54309E35621CAA925
• 45C1B556F5A875B71F2286E1ED4C7BD32E705758
• 682389250D914B95D6C23AB29DFFEE11CB65CAE9
• 7895E4D017C3ED5EDB9BF92C156316B4990361EB
• 8118474606A68C03581EEF85A05A90275AA1EC24
• 66490C59CB9630B53FA3FA7125B5C9511AFDE38EDAB4459065938C1974229CA8
MITRE ATT&CK
ATT&CK Technique | Technique/Sub-Technique Title |
T1562.001 | Disable or Modify Tools |
T1204 | User Execution |
T1007 | System Service Discovery |
T1012 | Query Registry |
T1485 | Data Destruction |
T1069.002 | Domain Groups |
T1489 | Service Stop |
T1189 | Drive-by Compromise |
T1059.003 | Windows Command Shell |
T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information |
T1083 | File and Directory Discovery |
T1486 | Data Encrypted for Impact |
T1082 | System Information Discovery |
T1059.001 | PowerShell |
T1204.002 | Malicious File |
T1071.001 | Web Protocols |
T1140 | De-obfuscate/Decode Files or Information |
T1112 | Modify Registry |
T1055 | Process Injection |
T1106 | Native API |
T1490 | Inhibit System Recovery |
T1105 | Ingress Tool Transfer |
T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
T1070.004 | File Deletion |
T1547.001 | Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
T1566.001 | Spearphishing Attachment |
T1218.003 | CMSTP |
T1047 | Windows Management Instrumentation |
T1491 | Defacement |
Remediation and Mitigation Plan
• Patch operating systems, applications, and keep antivirus signatures up to date.
• Ensure the endpoint patched with this CVE-2021-30116.
• Scan emails and attachments to detect and block any suspicious malware activity.
• Implement training and processes to identify phishing & externally-sourced emails.
• Maintain offline, encrypted backups of data and regularly test backups.
• Conduct regular backup procedures and keep those backups offline or in separated networks.
References
- REvil ransomware hits 1,000+ companies in MSP supply-chain attack on July 2, 2021
- CISA-FBI Guidance for MSPs and their Customers Affected by the Kaseya VSA Supply-Chain Ransomware Attack on July 6, 2021
- Diving Deeper Into the Kaseya VSA Attack: REvil Returns and Other Hackers Are Riding Their Coattails on July 7, 2021











